TCSP ER-2 MODIS Airborne Simulator (MAS)
Table of Contents
Introduction
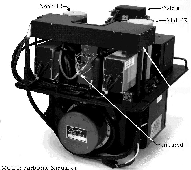 The MODIS Airborne Simulator (MAS) data were collected in support of The Tropical Cloud Systems and Processes mission (TCSP), conducted by NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) in Costa Rica throughout July 2005. The TCSC mission collected data for reasearch and documention of "cyclogenesis", the interaction of temperature, humidity, precipitation, wind and air pressure that creates ideal birthing conditions for tropical storms, hurricanes and related phenomena. The goal of this mission was to help us better understand how hurricanes and other tropical storms are formed and intensify. The MODIS Airborne Simulator (MAS) data were collected in support of The Tropical Cloud Systems and Processes mission (TCSP), conducted by NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) in Costa Rica throughout July 2005. The TCSC mission collected data for reasearch and documention of "cyclogenesis", the interaction of temperature, humidity, precipitation, wind and air pressure that creates ideal birthing conditions for tropical storms, hurricanes and related phenomena. The goal of this mission was to help us better understand how hurricanes and other tropical storms are formed and intensify.
The MODIS Airborne Simulator (MAS) is a scanning spectrometer which flies on a NASA ER-2 high altitude research aircraft. It measures reflected solar and emitted thermal radiation in 50 narrowband channels between 0.46 and 14.3 microns (specifications). MAS produces image data with 50 meter resolution (at nadir) across a 37 kilometer ground swath from a nominal altitude of 20 kilometers.
Instrument Description
The MAS is a multi-spectral line-scanning spectrometer that acquires image data in 50 spectral bands over wavelengths ranging from 0.46 to 14.3 microns. Flown on an ER-2 aircraft at an operating altitude of 19.8 kilometers (65,000 ft.) it produces image data with 50 meter resolution (at nadir), across a 37 kilometer ground swath. MAS includes nine spectral bands in the visible/near infrared, 16 bands in the shortwave infrared, 16 bands in the mid-wave infrared, and nine bands in the thermal infrared regions of the spectrum. The instrument field-of-view is 86 degrees, with an IFOV of 2.5 mrad.
Additional information may be found here.
Documentation
Extensive documentation about the instrument, calibration, geolocation and data extraction can be found in the MAS Level-1B Data User's Guide, as supplied by the AMES MODIS Airborne Simulator Documents and Research web site: http://mas.arc.nasa.gov/reference/guide.html
Data Description and Format
MAS data were collected continuously at 6.25 scans per second during an ER-2 flight (at altitude). Only straight and level flight tracks were archived. Each file represents a unique time segment from a particular flight.
The MAS data resolution consists of 50 meter pixels at nadir, at 19.8 km altitude. Swath width is 36 km (across-track).
The data are processed to Level-1B geo-located multi-spectral visible and infrared imagery and calibrated to at-sensor radiance of watts/meter2/steradian/micron. The data are in HDF format (version 4.1.4).
File Naming
The data files for each ER-2 flight have been compressed via "gzip", and bundled into a single "sortie" file via the unix "tar" command, and they look like this:
tcspmas_yyyy.ddd_05fff.tar
Where "yyyy.ddd" is the year and 'day of year', and "05fff" is the ER-2 sortie number. This tar file will contain all HDF data files for the sortie, all browse files for the sortie, a trackmap file showing the flight path, a flight summary file, and a nadir profile file for the flight. Example files included in each bundle are:
Data: MASL1B_05921_01_20050618_1421_1433_V01.hdf.gz
<instr + processing level>_<sortie>_<track>_<date (yyyymmdd)>_<start time (hhmm)>_<end time (hhmm)>_<version number>.<HDF format>.<compressed via gzip>
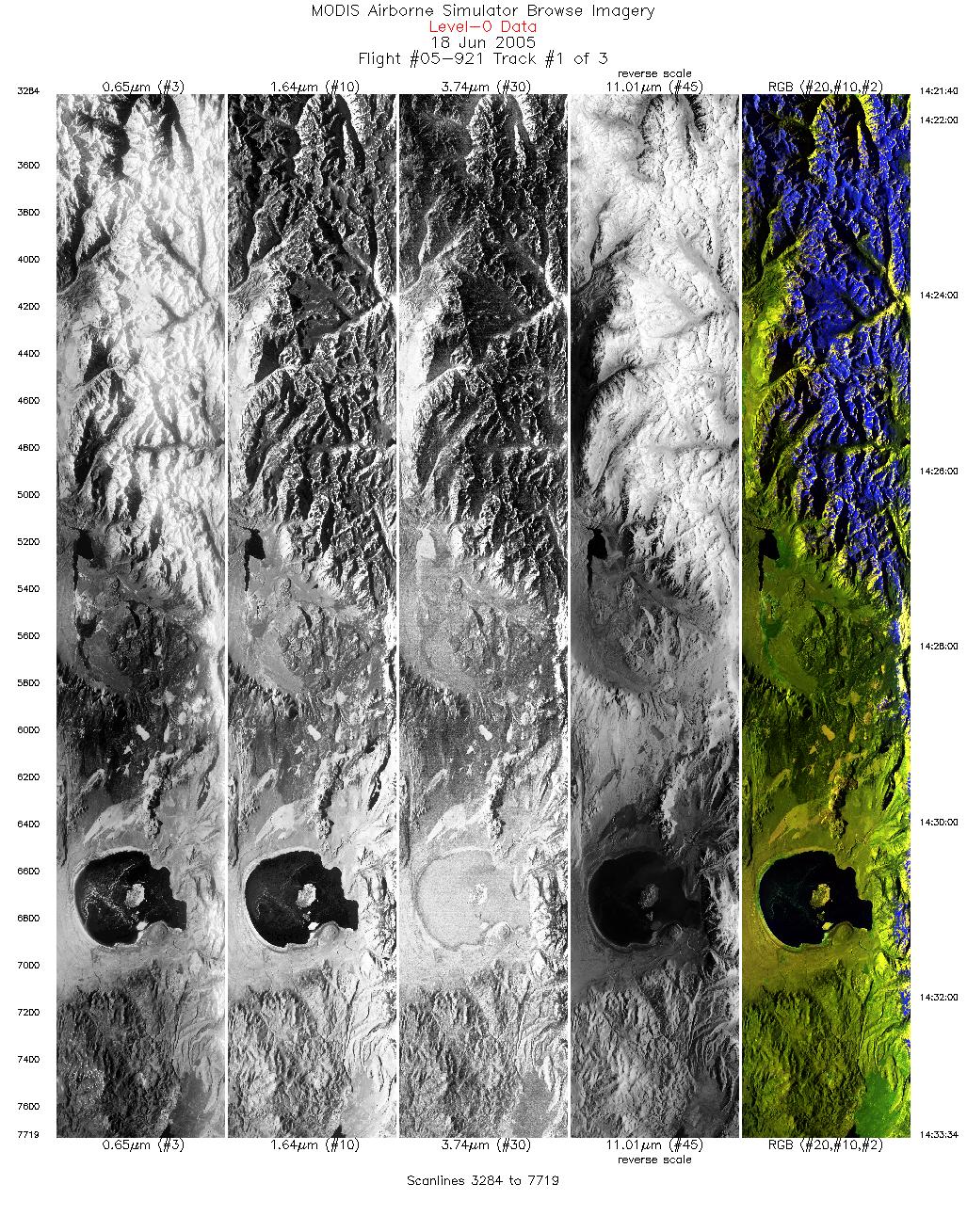
Browse: tcspmas_05921_01.jpg
<fieldexp-inst>_<sortie#>_<sequence number>.jpg
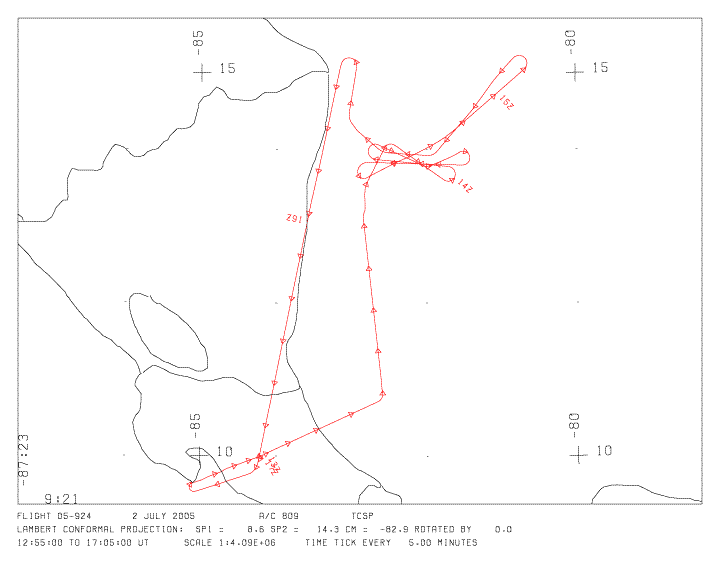
Flight track: tcspmas_05921tm.gif
<fieldexp-inst>_<sortie#><track map>.gif
Nadir profile: tcspmas_05921.Nadir.txt
<fieldexp-inst>_<sortie#><Nadir>.txt
Summary: tcspmas_05935.sum
<fieldexp-inst>_<sortie#>.sum
Each flight contains a flight information (sumary) file in ASCII format with the extension .sum. These files give information on each of the flight tracks (lat, lon, time, solar elevation and azimuth and aircraft heading at the start of the track) as well as what are called 'Global Attributes'. Global Attributes include mission specific information (aircraft, dates, etc.). An example is shown below:
Each flight also has a Nadir profile file, which list the processing inputs for the 50 channel scanner, using 2 visual and 2 IR nadir pixel bands.
There is a flight path browse, in 'gif' format, as shown at the right. Also included is a browse of the data, in 'jpg' format, one for each track during the sortie. An example browse is shown below, which was taken over Mono Lake, CA. This is browse file tcspmas_05921_01.jpg.
Note that the naming convention describes a jpg image from MAS during the TCSP experiment, mission number 05-921, the first track.
Software
MAS Level-1B data are stored in Hierarchical Data Format, version 4, (HDF4), and should only be accessed through the proper HDF4 librarys. HDF software is available from NCSA through their web site: http://hdf.ncsa.uiuc.edu/. Both IDL/ENVI and MatLab can be used to read MAS HDF data. General help on how to read these data, and other available software, can be found at the following AMES web site: http://mas.arc.nasa.gov/reference/unpacking.html.
References
King, M. D., W. P. Menzel, P. S. Grant, J. S. Myers, G. T. Arnold, S. E. Platnick, L. E. Gumley, S. C. Tsay, C. C. Moeller, M. Fitzgerald, K. S. Brown and F. G. Osterwisch, 1996: Airborne scanning spectrometer for remote sensing of cloud, aerosol, water vapor and surface properties. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol., 13, 777-794.
Arnold, G.T., M. Fitzgerald, P.S. Grant, and M.D. King, 1994a: MODIS Airborne Simulator Visible and Near-Infrared Calibration - 1991 FIRE-Cirrus Field Experiment. NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, NASA Technical Memorandum 104600.
Arnold, G.T., M. Fitzgerald, P.S. Grant, and M.D. King, 1994b: MODIS Airborne Simulator Visible and Near-Infrared Calibration - 1992 ASTEX Field Experiment. NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, NASA Technical Memorandum 104599.
Jedlovec, G.J., K.B. Batson, R.J. Atkinson, C.C. Moeller, W.P. Menzel, and M.W. James, 1989: Improved Capabilities of the Multispectral Atmospheric Mapping Sensor (MAMS). NASA Marshall Space Flight Center, NASA Technical Memorandum 100352.
King, M. D., Y. J. Kaufman, W. P. Menzel and D. Tanré, 1992: Remote sensing of cloud, aerosol, and water vapor Properties from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectrometer (MODIS). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 30, 2-27
Contact Information
To order these data or for further information, please contact:
Global Hydrology Resource Center
User Services
320 Sparkman Drive
Huntsville, AL 35805
Phone: 256-961-7932
E-mail: support-ghrc@earthdata.nasa.gov
Web: http://ghrc.nsstc.nasa.gov/
|

