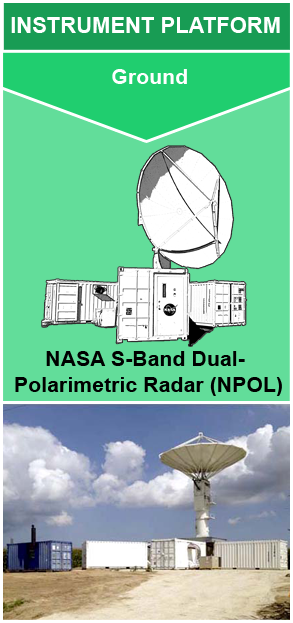
Instrument: NASA S-band Dual Polarimetric Radar (NPOL)
The NASA S-band Dual Polarimetric Radar (NPOL) is a research grade S-band, scanning dual polarimetric Doppler radar. It has equivalent capabilities to the Doppler radars of the U.S. National Weather Service’s Next Generation Weather Radar (NEXRAD) network. However, in contrast to the stationary NEXRAD radars, NPOL is one of two completely transportable research-grade S-band systems in the world. The radar operates atop a pedestal and 5 intermodal containers (i.e., sea containers) and is stored inside these containers when being transported for deployment. NASA’s NPOL weather radar has been and continues to be used for various NASA field campaigns. It resides and operates near NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Newark, MD when not on field campaign deployment.

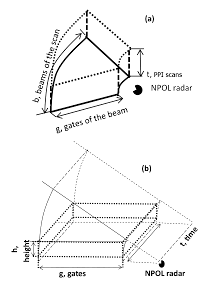
Measures radar reflectivity, Doppler velocity, differential reflectivity, correlation, differential phase, rainfall rate, particle size distribution, water contents and precipitation type. When the radar antenna is wet, this can increase signal attenuation and lead to data quality issues. Self-consistency and disdrometer comparisons are used to estimate the absolute calibration of NPOL. Also, the pointing angle of the radar dish is monitored with software that uses the sun’s position to calibrate the elevation and azimuth angles.
| FREQUENCY | SPATIAL EXTENT | BEAM WIDTH | ACCURACY | PULSE REPETITION FREQUENCY (PRF) | ANTENNA | GAIN | PULSE WIDTH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
2.7 - 2.9 GHz (10.65 cm wavelength) |
150 km range | 0.95° | 0.1° pointing accuracy | 500 - 1000 Hz | 8.5 m |
45.8 dB (+/- 0.3 dB) |
0.8 - 2.0 ms |
Bringi, V.N., L. Tolstoy, M. Thurai, & Petersen, W.A. (2015). Estimation of Spatial Correlation of Drop Size Distribution Parameters and Rain Rate Using NASA’s S-Band Polarimetric Radar and 2D Video Disdrometer Network: Two Case Studies from MC3E. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 16, 1207–1221. https://doi.org/10.1175/JHM-D-14-0204.1